7 Proven Benefits of Edge Computing for Boosting Efficiency
Introduction
In today’s hyper-connected world, businesses are increasingly turning to edge computing to enhance operational efficiency, speed up data processing, and bolster data security. With the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, 5G networks, and real-time data requirements, traditional cloud computing systems can no longer handle the volume and speed of data being generated. That’s where edge computing comes in, offering a decentralized approach that brings data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and enabling faster, smarter decision-making.
This article delves into the proven benefits of edge computing that make it a game-changer for businesses aiming to optimize their operations, improve user experiences, and stay competitive in an increasingly data-driven landscape.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a distributed IT architecture where data processing happens near the source of data rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. This computing model involves deploying small, decentralized data centers or edge devices that handle data processing locally, minimizing the need for data to travel to a distant cloud. By reducing the distance data must travel, edge computing dramatically lowers latency, improves response times, and enhances the reliability of applications that require real-time data processing.
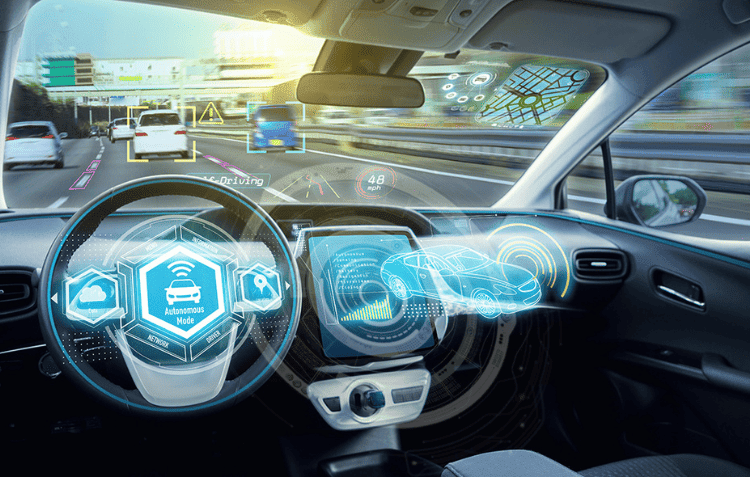
For instance, in an autonomous vehicle, real-time decisions such as braking or steering cannot afford the delays inherent in sending data to a remote cloud for processing. With edge computing, these decisions can be made on the spot, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Key Differences Between Edge and Cloud Computing
- Edge Computing: Decentralized processing occurs near the data source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage.
- Cloud Computing: Centralized processing in data centers, requiring data to travel longer distances, which may introduce latency.
Edge computing complements cloud computing by handling time-sensitive data locally while still relying on the cloud for deeper analysis and storage.
Proven Benefits of Edge Computing
1. Reduced Latency and Faster Decision Making
Latency is a critical factor in applications where real-time data processing is essential. In industries like autonomous driving, healthcare, and industrial automation, even a few milliseconds of delay can be detrimental. Edge computing reduces latency by processing data closer to its source, allowing for faster decision-making and improved user experiences.
For example, smart traffic management systems in cities rely on real-time data from IoT devices such as cameras and sensors. If data were sent to a cloud server for processing, there would be delays in adjusting traffic lights or redirecting traffic. With edge computing, these systems can make instant decisions based on local data, improving traffic flow and reducing congestion.
Real-World Use Case: Autonomous Vehicles
In self-driving cars, every millisecond matters. Edge computing allows onboard systems to process vast amounts of sensor data in real-time, making instant decisions that ensure the vehicle’s safety. This local processing eliminates the need for constant communication with a central server, reducing the risk of delayed responses.
2. Enhanced Data Security and Privacy
Data security has become a significant concern as more devices connect to the internet, leading to an explosion of sensitive information being transmitted across networks. Edge computing offers enhanced security by reducing the amount of sensitive data that must travel across public networks to centralized cloud servers. Instead, data is processed locally, lowering the risk of interception or hacking during transmission.
Additionally, edge computing allows businesses to implement better data privacy controls by keeping personal or sensitive data close to its source. For instance, healthcare providers can process patient data locally on secure edge devices rather than sending it to a cloud where it may be more vulnerable to cyberattacks. This also helps organizations comply with privacy regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
Real-World Use Case: Healthcare
Edge computing plays a vital role in healthcare, especially with the increasing use of wearable health devices that track vital signs in real-time. Processing patient data locally ensures that sensitive medical information stays secure while also enabling healthcare providers to make quick decisions, such as alerting doctors about abnormal health metrics without delay.
3. Cost-Effective Operations
Implementing cloud computing infrastructure can be expensive, especially when dealing with the massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices. Edge computing helps reduce operational costs by lowering the need for bandwidth and storage in centralized data centers. Since much of the data processing happens locally, only essential information is transmitted to the cloud, minimizing the load on cloud servers and reducing costs.
In addition to bandwidth savings, edge computing can extend the life of existing IT infrastructure. By offloading processing tasks to edge devices, businesses can reduce the strain on their central servers and avoid costly upgrades to their cloud infrastructure.
Real-World Use Case: Retail
In the retail industry, edge computing can optimize customer experiences and inventory management. For instance, in-store IoT devices can track inventory levels in real-time and adjust stock automatically. These local processes eliminate the need to send vast amounts of data to a central cloud server, reducing bandwidth usage and cloud storage costs.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
Edge computing is inherently scalable, making it easier to handle the growing number of IoT devices generating data. Unlike traditional centralized systems, which can become overwhelmed by the volume of data being transmitted, edge computing distributes the workload across numerous edge devices, ensuring that networks do not become congested.
Moreover, edge computing offers businesses greater flexibility in how they deploy and manage their IT resources. By processing data locally, businesses can quickly adapt to changing operational requirements without overburdening their central infrastructure.
Real-World Use Case: Smart Cities
In smart cities, where millions of IoT devices are deployed to monitor traffic, energy consumption, and public safety, edge computing helps distribute the data processing load. By processing information locally at the edge, smart city systems can scale seamlessly, handling the increasing volume of data without overloading centralized systems.
5. Improved Reliability and Availability
Centralized cloud systems can experience outages or disruptions, leading to downtime for critical applications. Edge computing improves reliability by decentralizing data processing, ensuring that local applications continue to function even if there’s an issue with the cloud. By processing data locally, edge computing reduces the reliance on a constant connection to the cloud, ensuring that services remain available even during network interruptions.
For mission-critical applications like industrial automation or emergency response systems, the ability to process data locally can mean the difference between success and failure.
Real-World Use Case: Industrial IoT
Manufacturing facilities use IoT sensors to monitor equipment performance and predict maintenance needs. If these sensors had to send all their data to the cloud for analysis, any network disruptions could halt production. With edge computing, data is processed locally, ensuring continuous operation even during network outages.
6. Real-Time Analytics and Insights
Edge computing enables real-time data analytics, allowing businesses to gain immediate insights without waiting for data to be processed in the cloud. This is particularly valuable in industries like finance, where real-time decision-making is critical, or in manufacturing, where predictive maintenance systems rely on immediate data to prevent costly equipment failures.
By processing data locally, edge computing enables businesses to act on insights as soon as they are generated, improving operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
Real-World Use Case: Predictive Maintenance
In manufacturing, predictive maintenance systems use data from sensors to anticipate equipment failures before they happen. Edge computing allows these systems to analyze sensor data in real-time, providing immediate insights that can help prevent downtime and extend the life of machinery.
7. Optimized Network Bandwidth Usage
With the growing number of connected devices and the increasing amount of data they generate, network bandwidth is a valuable resource. Edge computing optimizes bandwidth usage by reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to a central cloud. Only essential data is sent for further analysis, while the bulk of the processing happens locally.
This bandwidth efficiency is especially important in remote areas or locations with limited network capacity, where sending large amounts of data to the cloud is not feasible.
Real-World Use Case: Agriculture
In precision agriculture, edge computing helps farmers monitor crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns using IoT devices. These devices process data locally, only transmitting relevant insights to the cloud, reducing bandwidth usage and ensuring efficient farm management.
Applications of Edge Computing
Edge computing’s benefits extend across various industries, from smart cities and healthcare to retail and manufacturing. Below are some of the key applications where edge computing is driving efficiency:
- IoT and Smart Devices: Enhances the performance of IoT devices by processing data locally.
- 5G Networks: Powers faster, low-latency communication for real-time analytics.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Enables real-time decision-making for safer, more efficient driving.
- Smart Cities: Supports traffic management, public safety, and energy conservation by processing data at the edge.
- Healthcare: Improves patient care through real-time health monitoring and analysis.
Conclusion
Edge computing is transforming industries by delivering faster, more efficient, and secure data processing closer to the source. Its ability to reduce latency, enhance data security, lower costs, and improve scalability makes it an essential technology for businesses looking to optimize their operations and stay competitive in today’s digital landscape. As the world continues to embrace IoT, 5G, and real-time analytics, the benefits of edge computing will only become more apparent, driving innovation across all sectors.
By embracing edge computing, businesses can boost efficiency, improve decision-making, and create more responsive, reliable systems that are built to thrive in the data-driven future.
FAQs
What are the benefits of using edge computing?
Edge computing improves efficiency by processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. It enhances real-time performance for applications like IoT, while increasing data privacy by keeping sensitive data local. This results in faster, more reliable services with lower costs.
What are the benefits of 5G edge computing?
5G combined with edge computing enables ultra-low latency, supporting real-time applications such as autonomous vehicles and remote healthcare. It also increases network capacity for handling large data volumes and offers improved scalability for IoT devices, ensuring more robust and efficient connectivity.
What are the benefits of edge AI?
Edge AI processes data locally on devices rather than in the cloud, leading to faster decision-making and real-time analytics. It enhances privacy by keeping sensitive data on-premises and reduces reliance on internet connectivity, making it ideal for autonomous systems and smart devices.
What are examples of edge computing?
Common examples include autonomous vehicles, which process sensor data locally to make real-time decisions, and smart cities, where edge devices control traffic lights based on live conditions. Other applications include industrial IoT for predictive maintenance and AR/VR for immersive experiences.
What are the pros and cons of edge?
Pros: Edge computing reduces latency, lowers bandwidth costs, and enhances data privacy and real-time processing.
Cons: It can involve higher hardware costs, complex infrastructure management, and potential security challenges due to decentralized data handling.